Connecticut, renowned for its picturesque landscapes and thriving communities, faces a challenge that transcends its scenic beauty—the pervasive issue of depression. Depression, a mental health condition that knows no boundaries, impacts individuals from all walks of life. In this comprehensive article, we will delve into the landscape of depression in Connecticut, shedding light on its prevalence, consequences, available resources, and the collective efforts to address this critical issue.
The Prevalence of Depression in Connecticut
Depression, clinically referred to as major depressive disorder (MDD), manifests as persistent feelings of sadness, hopelessness, and a diminished interest or pleasure in daily activities. This mental health condition affects individuals of all ages, backgrounds, and socioeconomic statuses. In Connecticut, like many other regions across the United States, depression stands as a substantial public health concern.
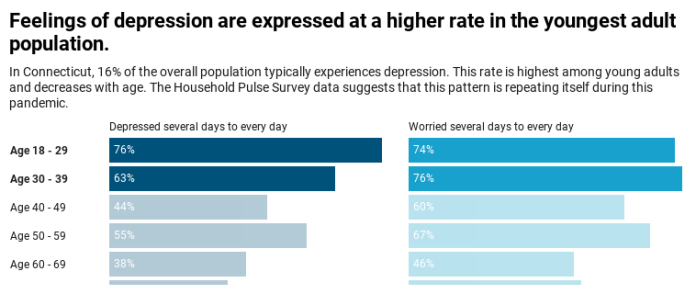
Data from the Substance Abuse and Mental Health Services Administration (SAMHSA) reveals that an estimated 6.7% of adults in Connecticut experienced at least one major depressive episode in the past year. This prevalence underscores the significance of recognizing and addressing depression as a pivotal mental health issue in the state.
The Impact of Depression on Individuals and Communities
Depression casts a far-reaching shadow, affecting not only individuals but also entire communities. In Connecticut, it influences not only the mental and emotional well-being of those directly affected but also their physical health and overall quality of life. Common symptoms of depression encompass:
- Persistent sadness or a pervasive low mood
- Loss of interest or pleasure in once-enjoyed activities
- Fluctuations in appetite or weight
- Sleep disturbances, ranging from insomnia to excessive sleep
- Profound fatigue or low energy levels
- Feelings of worthlessness or overwhelming guilt
- Challenges concentrating or making decisions
- Thoughts of death or suicide
Depression can lead to a cascade of adverse consequences, including:
- Impaired Daily Functioning: Individuals grappling with depression often find it arduous to carry out routine tasks, maintain employment, or engage in social interactions.
- Physical Health Complications: Depression frequently coexists with physical health issues, such as chronic pain, heart disease, and a compromised immune system.
- Elevated Risk of Suicide: Severe depression constitutes one of the primary risk factors for suicide, underlining the imperative of early intervention and treatment.
- Impact on Families: Depression can strain relationships and exert a profound toll on family members and caregivers.
- Economic Burden: The economic weight of depression, including healthcare costs and lost productivity, is substantial.
Addressing Depression in Connecticut
Connecticut has embarked on a determined journey to confront depression and enhance access to mental health services for its residents. Key initiatives and resources encompass:
- Mental Health Parity Laws: Connecticut has instituted mental health parity laws, mandating that insurance providers offer equal coverage for mental health and physical health services. This legislative stride has increased access to depression treatment while reducing financial barriers.
- Community Mental Health Centers: The state is home to a network of community mental health centers that provide a wide spectrum of services, including the diagnosis and treatment of depression. These centers serve as vital lifelines for individuals seeking support.
- Hotlines and Crisis Intervention: Connecticut extends hotlines and crisis intervention services for individuals in urgent need of assistance. These resources offer immediate support and link individuals with suitable mental health professionals.
- School-Based Mental Health Services: Many schools Depression in Connecticut offer mental health services to students, recognizing the significance of early intervention in addressing depression and related concerns.
- Non-Profit Organizations: Non-profit entities in Connecticut, such as the Connecticut Alliance to Benefit Law Enforcement (CABLE), focus on bolstering mental health awareness and support for law enforcement officers and their families, acknowledging the distinctive challenges they face.
Promoting Mental Health Awareness in Connecticut
To effectively combat depression, Connecticut has prioritized the promotion of mental health awareness and the reduction of stigma. Assorted campaigns and initiatives are in motion to encourage individuals to seek help and lend support to their loved ones. The state underscores that early intervention and destigmatization are pivotal components in effectively addressing depression.
Conclusion
Depression represents a significant mental health challenge in Connecticut, impacting a substantial portion of its population. Nonetheless, the state refuses to be passive in the face of this issue. Connecticut has taken substantial strides to augment access to mental health services, diminish stigma, and amplify awareness of depression. By placing mental health and well-being at the forefront, Connecticut aspires to equip its residents with the support and resources indispensable for navigating the intricacies of depression and attaining mental wellness.