Introduction:
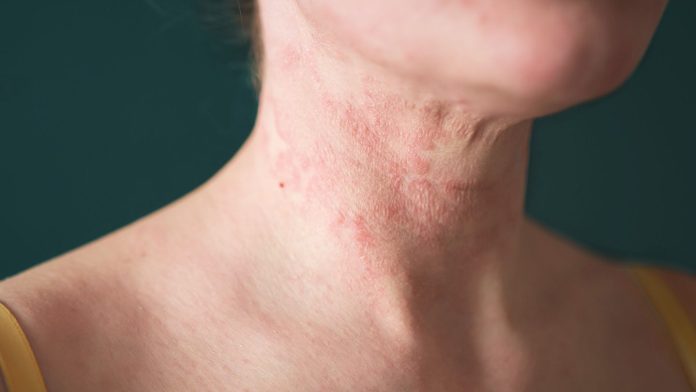
Atopic dermatitis cases frequently have dry, itchy skin that breaks, bleeds, or becomes infected. This composition covers atopic dermatitis treatments and home remedies, the rearmost medical exploration, tips for treating the condition, and more. Atopic dermatitis, generally known as eczema, is a long- term (chronic) condition that makes the skin inflamed, red, and bothered.
It’s a common condition that generally begins in non-age, but the complaint can spread to anyone and at any age. While scientists don’t know what causes atopic dermatitis, they do know that genetics, the vulnerable system, and environmental factors play a part in the disease.
For most people, atopic dermatitis clears up with age, but for some, it can be a lifelong condition. Light remedy for atopic dermatitis can help people get relief from this complaint.
Who Gets Atopic Dermatitis?
Atopic dermatitis is a common condition that generally appears in immaturity and childhood. In numerous children, atopic dermatitis disappears before puberty. In some children with atopic dermatitis, symptoms may continue into non age and majority. Sometimes the disease first appears in some people later in life.
The chance of developing atopic dermatitis is lesser if there’s atopic dermatitis, hay fever, or asthma in your family. Atopic dermatitis (eczema) is a condition in which the skin becomes dry, itchy, and inflamed. It’s more common in children, but it can be done at any age. Atopic dermatitis is a habitual complaint that occasionally worsens.
Causes of Atopic Dermatitis
No one knows what causes atopic dermatitis; still, scientists know that changes in the skin’s defensive layer can lead to dehumidification. It dries the skin and causes inflammation. Atopic dermatitis (eczema) is one of numerous types of skin infections.
New research suggests that the inflammation immediately triggers itching, causing patients to vomit. This not only further damages the skin but also increases the threat of infection. Scientists know that the skin’s humidity- control hedge changes as follows.
- Genetic changes (nutation).
- Problems with the immune system.
- Discover certain objects in the environment.
Genetics
Atopic dermatitis is more likely if the complaint runs in families, suggesting that genetics may play a part in the complaint. Scientists have lately discovered mutations in the genes that control a certain protein that helps our bodies maintain a healthy layer of skin.
Without enough of this protein, the skin barrier changes, causing the skin to leak and expose the skin’s immune system to the environment, leading to atopic dermatitis.
Immune System
The entire immune system helps the body fight disease, bacteria and viruses. Sometimes the immune system becomes confused and overactive, causing skin inflammation and atopic dermatitis.
Environment
Environmental factors activate the immune system and change the skin’s protective barrier, increasing secretion and leading to atopic dermatitis. This may include
- Stop smoking.
- Some air pollutants.
- Fragrances and other ingredients in skin care products and soaps.
- Very dry skin.
Treatments for Atopic Dermatitis
Light therapy for atopic dermatitis uses special lights or spotlights. It can safely and effectively treat atopic dermatitis, indeed in children. Eczema treatment options include:
- Emollients (moisturisers) for treating atopic dermatitis
Emollients moisturize the skin. Use a daily moisturizer for clear, dry skin. Bathing Drinking water after showering is very important, as it is when you live or work in an air-conditioned or hot environment. You need to try numerous different brands of fabric quieter until you find the bone that works better for you.
- Coal tar for treating atopic dermatitis
Applying coal navigator to the affected areas is another way to reduce the itching of dermatitis. Coal navigator has a strong odor and begins to stain the clothes it touches. It can also cause skin vexation in some people.
- Oral corticosteroids
Most people with atopic dermatitis can overcome the condition simply by using creams and ointments. While oral corticosteroids can help people with resistant atopic dermatitis, side goods include high blood pressure, vulnerability to all kinds of infections, and mood and behavioural changes.
- Ultraviolet radiation therapy (phototherapy) for atopic dermatitis
Exposure can be effectively controlled under medical supervision using special “colhons”: underwear is worn on a mattress while fluorescent tubes emit UV light.
A person with habitual dermatitis may need 30 treatments spread out 2- 3 times a week. Dangers from the sun can also accelerate skin aging and increase the threat of skin cancer.
- Anti-inflammatory ointments for treating atopic dermatitis
Atopic dermatitis responds well to anti-inflammatory specifics. Topical steroids (corticosteroids) vary in strength and are available by tradition. In general, it’s best to use the minimum effective power.
Long- term use of largely potent steroids, especially in sensitive areas similar as the face, can cause side effects, including skin blankness. Severe cases of eczema may bear short courses of oral corticosteroids.
Conclusion.
Although there’s presently no cure for atopic dermatitis, people can manage their symptoms with a combination of treatments. These include topical creams, oral specifics, moisturizing compresses, phototherapy, and special cataracts. Light remedy for atopic dermatitis reduces the threat of skin infections due to itching and blankness.